What is Fanconi Anemia?
The disease was described by Fankoni in 1927 in 3 children in the same family. Since that time, many family cases have been described.
Causes of Fanconi Anemia
Inheritance of the disease is autosomal recessive, it is manifested in homozygotes. Anemia is sometimes found from birth, but more often after 5 years.
Pathogenesis during Fanconi Anemia
Most likely, with Fanconi anemia, there is a defect in stem cells. It was proved that neither the serum of patients with Fanconi anemia, nor their lymphocytes do not affect the efficiency of colony in the cultivation of bone marrow donors.
A defect was established in the DNA repair system in fibroblasts of patients with Fanconi anemia. Most likely, this is the reason for the slight damage to the chromosomes during this disease under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, small doses of cytostatic drugs.
Symptoms of Fanconi Anemia
Fanconi anemia is rarely seen at birth. The first manifestations of the disease are noted already at the age of 4-10 years, usually boys are more likely to suffer. Anemia appears gradually, the first symptoms are bleeding and bruising.
In parallel with these manifestations, an increased tendency to infections develops. The liver and spleen are usually not enlarged. In most cases, the size of the lymph nodes is normal, but sometimes lymphadenopathy is found due to infection.
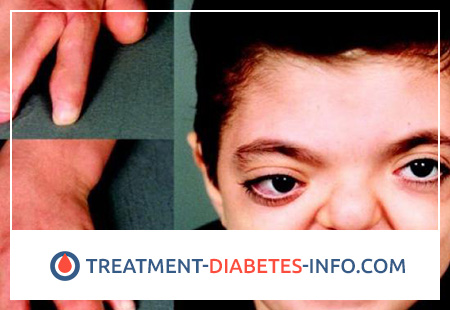
There are other anomalies associated with anemia. Most often it is abnormal pigmentation, short stature, small head, skeletal deformities (absence or shortening of the thumb, hypoplasia of the radius, congenital dislocation of the hip, cervical rib, clubfoot). In addition, a number of neurological disorders (strabismus, underdevelopment of one or both eyes, eyelid omission, eye tremor, deafness, mental retardation), damage to the genital organs (underdevelopment of the genital organs, absence of one or both testicles, hypospadias), renal deformities (renal development , doubling of the pelvis or ureter, horseshoe kidney, multiple cysts in the tissues of the kidneys), congenital heart defects.
In children suffering from Fanconi anemia, increased propensity for the disease of acute leukemia.
Diagnosis of Fanconi Anemia
Changes in the blood resemble those observed in the idiopathic form of aplastic anemia, but are often less pronounced, especially for the platelet sprout. However, with Fankoni anemia, there may be a noticeable thrombocytopenia, typically a significant increase in fetal hemoglobin. In half of the children with Fanconi anemia in the urine an elevated amino acid content is found. There are changes in chromosomes: the exchange of chromatids, breakdowns of chromatids and endoreduplications. The number of chromosomes remains normal. These chromosomal changes are observed not only in myeloid, lymphoid cells, but also in fibroblasts.
Treatment for Fanconi Anemia
If a link between aplastic anemia and individual intolerance of a drug is suspected, urgent withdrawal of the drug is necessary. Treatment of idiopathic aplastic anemia depends largely on its severity. In severe aplastic anemia, the bone marrow is less than 35%, and there are at least 2 out of 3 signs: platelets are less than 20 × 109 / l, neutrophils are less than 0.5 * 109 / l, and reticulocytes after correction are less than 1%.
An anti-lymphocyte globulin is used to treat aplastic anemia after unsuccessful spleen removal and treatment with anabolic steroids.
Removal of the spleen with subsequent treatment with anti-lymphocytic globulin was effective not only in the idiopathic form of aplasia, but also in aplasia that occurred after acute viral hepatitis.
Sometimes treatment with immunosuppressive drugs (cyclophosphamide, methotrexate). With the introduction of these drugs there is a danger of increased bleeding, the appearance of inflammatory foci, although treatment with cyclophosphamide, especially after the removal of the spleen, is effective in a number of patients.
One of the main methods of treating severe aplastic anemia remains bone marrow transplantation from donors selected by the HLA system and MLC. The most favorable transplantation from identical twins. In these cases, sometimes it is possible to transplant without prior immunosuppression, mandatory before bone marrow transplantation. Bone marrow is usually taken from a patient’s brothers or sisters. For the prevention of rejection, cyclophosphamide in a large dose (50 mg / kg per day) for 3 days, anti-lymphocyte globulin is used. The efficiency of transplantation is higher, the fewer blood transfusions.
One of the serious complications of transplantation is a secondary graft-versus-host disease, manifested as lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and skin.
Currently, the main difficulty lies in the selection of a donor, especially with a small number of children in families.
Forecast
With the help of bone marrow transplantation, more than half of patients with severe aplastic anemia can be helped. Removal of the spleen with subsequent treatment with anabolic hormones, anti-lymphocytic globulin leads to the improvement of the condition of almost half of patients with severe anemia. A large amount of fat in the bone marrow does not mean that the process is irreversible. Sometimes, in such patients, significant improvement and full restoration of bone marrow hematopoiesis occurs. The prognosis is better with an increase in the content of reticulocytes, a normal ratio between the fractions in the bone marrow, at least a small number of megakaryocytes and some effect from prednisolone. In these cases, removal of the spleen helps.
One of the outcomes of aplastic anemia is hemolytic anemia with intravascular erythrocyte destruction, resembling Markiafav-Mikeli disease.
In some patients, aplastic syndrome becomes the beginning of acute leukemia. Sometimes signs of hemoblastosis are detected only a few years after the onset of the disease.